lv thrombus vs demonstrable lv thrombus | Lv thrombus risk management lv thrombus vs demonstrable lv thrombus eLetters should relate to an article recently published in the journal and are not a .
Fakes are made from pleather and vinyl; they may feel rough and stiff. A real Louis Vuitton is smooth and feels soft. Trim: Louis Vuitton trim is done in Vachetta leather and tans naturally as the bag ages. Most fakes are done in a light tan trim or a fake aged trim that will not change with age.How to tell if Louis Vuitton is real (or fake) Bags: Check the “LOUIS VUITTON ®” inscription engraved in leather. Fake bags always have thicker text. Footwear: Verify the inscriptions on the soles. Fake shoes always have too little space in-between the text. Clothing: Look at the wash tags. A fake Louis Vuitton always has very thick prints.
0 · laminated Lv thrombus
1 · Lv thrombus topics
2 · Lv thrombus risk management
3 · Lv thrombus risk assessment
4 · Lv thrombus recurrence rate
5 · Lv thrombus morphology
6 · Lv thrombus heart attack
7 · Lv thrombus echocardiogram
piepras ījumu (Ekstraneta pieteikums atrodams m ājas lapas www.neste.lv sada ļā Ekstranet s) uz SIA „Neste Latvija” adresi Bauskas iel ā58a, R īgā, LV 1004, pa faksu 66013390 vai ar drošu elektronisko parakstu parakst ītu iesniegumu uz e - pasta adresi [email protected]. Iesniegum ājānorāda klienta numurs, e
The consensus of this writing group, which is based on retrospective registry data and small, prospective observational studies, is for anticoagulation (VKA or DOAC) in patients with LV thrombus in the setting of DCM for at least 3 to 6 months, with discontinuation if LVEF .¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
hoge dior sneaker
¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .Left ventricular (LV) thrombus formation is a well‐known complication in the course of .eLetters should relate to an article recently published in the journal and are not a .We sought to determine whether an association existed between the .
The following are key points to remember about this scientific statement from the American Heart Association (AHA) for the management of patients at risk for and with left .
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of .Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. . DOAC vs. Warfarin for LV Thrombus •3 center cohort study of 514 patients with LV thrombus (2013-2019) JAMA Cardiol 2020:5:685-692 aHR 2.64 (1.28-5.43) Key .
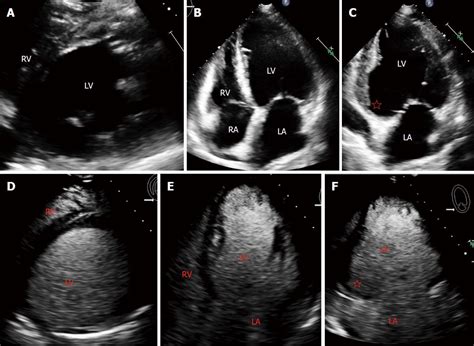
This pilot echocardiographic study of 52 patients has demonstrated that deformation imaging can be used to differentiate fresh and old intracavitary LV thrombi after myocardial infarction and has shown a correlation between .Accurate detection of left ventricular (LV) thrombus is important, as thrombus provides a substrate for thromboembolic events and a rationale for anticoagulation. Non-contrast echocardiography .Mechanistically, LV thrombus development depends on Virchow’s triad (ie, endothelial injury from myocardial infarction, blood stasis from LV dysfunction, and hypercoagulability triggered by inflammation, with each of these elements . Patients with LVT were identified from the registry and stratified by treatment group (VKA vs DOAC), which was left to the discretion of the treating cardiologist. Echocardiographic .
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus has a higher incidence among patients with anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) when compared to other types of acute myocardial .
The consensus of this writing group, which is based on retrospective registry data and small, prospective observational studies, is for anticoagulation (VKA or DOAC) in patients with LV thrombus in the setting of DCM for at least 3 to 6 months, with discontinuation if LVEF improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major . The following are key points to remember about this scientific statement from the American Heart Association (AHA) for the management of patients at risk for and with left ventricular (LV) thrombus: Decisions concerning the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of LV thrombus remain challenging. Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk.
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. Traditionally, LV thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI).
DOAC vs. Warfarin for LV Thrombus •3 center cohort study of 514 patients with LV thrombus (2013-2019) JAMA Cardiol 2020:5:685-692 aHR 2.64 (1.28-5.43) Key Considerations: • Long follow up (median 418 days) • OAC cross-over (21% of VKA, 35% of DOAC) • Modest annual event rates (0.065 SSE/pt-year) • Different treatment periods This pilot echocardiographic study of 52 patients has demonstrated that deformation imaging can be used to differentiate fresh and old intracavitary LV thrombi after myocardial infarction and has shown a correlation between thrombus stiffness and thrombus age.
Accurate detection of left ventricular (LV) thrombus is important, as thrombus provides a substrate for thromboembolic events and a rationale for anticoagulation. Non-contrast echocardiography (echo) detects LV thrombus based on anatomical appearance.Mechanistically, LV thrombus development depends on Virchow’s triad (ie, endothelial injury from myocardial infarction, blood stasis from LV dysfunction, and hypercoagulability triggered by inflammation, with each of these elements representing potential therapeutic targets). Patients with LVT were identified from the registry and stratified by treatment group (VKA vs DOAC), which was left to the discretion of the treating cardiologist. Echocardiographic outcomes evaluated included resolution of thrombus size and time to . Left ventricular (LV) thrombus has a higher incidence among patients with anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) when compared to other types of acute myocardial infarction and is associated with worse prognosis. The management of LV thrombus diagnosis remains challenging.
The consensus of this writing group, which is based on retrospective registry data and small, prospective observational studies, is for anticoagulation (VKA or DOAC) in patients with LV thrombus in the setting of DCM for at least 3 to 6 months, with discontinuation if LVEF improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major . The following are key points to remember about this scientific statement from the American Heart Association (AHA) for the management of patients at risk for and with left ventricular (LV) thrombus: Decisions concerning the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of LV thrombus remain challenging. Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk.Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. Traditionally, LV thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI).
dior trui heren wit
DOAC vs. Warfarin for LV Thrombus •3 center cohort study of 514 patients with LV thrombus (2013-2019) JAMA Cardiol 2020:5:685-692 aHR 2.64 (1.28-5.43) Key Considerations: • Long follow up (median 418 days) • OAC cross-over (21% of VKA, 35% of DOAC) • Modest annual event rates (0.065 SSE/pt-year) • Different treatment periods This pilot echocardiographic study of 52 patients has demonstrated that deformation imaging can be used to differentiate fresh and old intracavitary LV thrombi after myocardial infarction and has shown a correlation between thrombus stiffness and thrombus age.Accurate detection of left ventricular (LV) thrombus is important, as thrombus provides a substrate for thromboembolic events and a rationale for anticoagulation. Non-contrast echocardiography (echo) detects LV thrombus based on anatomical appearance.Mechanistically, LV thrombus development depends on Virchow’s triad (ie, endothelial injury from myocardial infarction, blood stasis from LV dysfunction, and hypercoagulability triggered by inflammation, with each of these elements representing potential therapeutic targets).
Patients with LVT were identified from the registry and stratified by treatment group (VKA vs DOAC), which was left to the discretion of the treating cardiologist. Echocardiographic outcomes evaluated included resolution of thrombus size and time to .
laminated Lv thrombus
dior shop new york
Lv thrombus topics
Lv thrombus risk management
Received 366 Likes on 250 Posts. For anyone who needs an option that's available over the counter at a parts store, Valvoline makes a synthetic multi-vehicle transfer case fluid which is basically a low viscosity Mercon type fluid, almost identical to Mercon LV. Mercon LV has a viscosity (cSt @100C) of 6.0.
lv thrombus vs demonstrable lv thrombus|Lv thrombus risk management